Greenhouse Types
New concept of intensive agriculture
Top Greenhouses specializes in the relatively new concept of intensive agriculture which relates to the highly-controlled growth of produce in greenhouses.
Until the appearance of this new concept, most of the crop growth was done in the open fields, thus leaving the grower and his crops exposed to the fluctuations of nature. The weather conditions directly influenced the length and success of crop growth seasons – a growth system known as extensive seasonal agriculture.
The introduction of indoor crop growth in controlled climate conditions neutralizes the impact of weather hazards and, theoretically, enables year-round growth. This new approach marked the world’s introduction to the concept of intensive agriculture. A significant concept change, greenhouse production has become a new, technology-based industry, involving new types of technical equipment capable of achieving predictable results and profits.
The competitiveness in markets and the ever-increasing quality standards for growers have increased the importance of each small agricultural production unit. It is within these units that the advantages of the modern greenhouse are expressed – the ability to control crop growth, growth schedules and yield, almost regardless of external factors, while protecting the high quality of produce year-round and ensuring the farmer a stable flow of income.
Top Greenhouses’ control over crop growth parameters results in:
- Higher quality crops resulting in higher profits.
- Improved land utilization which leaves land resources for other purposes (i.e.; real estate development).
- Better-supervised production of organic and bio produce, without the use of pesticides.
- A substantial decrease in water and fertilizer use, as well as minimal exposure to infections and environmental hazards serving as a basis for the installation of recycling systems.
- The considerable economy in manpower, as compared with the labor required for tending to open fields, while providing year-round (not seasonal) employment.
- Improved ability to compete in export markets.
- A constant need for training and professional specialization which leads to the excellence of personnel.
- Soil-less Substrate
There are several methods of crop growth using soil-less substrate. By definition, this method has the purpose of avoiding soil quality and soil-related diseases and pests.
Growth in soil-less substrate requires a separation of the growth area within a container, isolated so the roots of the plant never come in contact with the local soil. Using this method, the plant roots grow in a limited area, while receiving controlled amounts of water and fertilizers according to the needs of the specific crop.
The types of soil-less substrate available are volcanic sinter, coconut chips, perlite, rock wool, and sawdust. Each type of substrate behaves differently in terms of the volume of air it contains and it’s capacity for absorption of water and fertilizers. The packing of the substrate kit has to be suitable for each type of crop.
Soil-less substrates are very sensitive and need to be washed and drained in order to maintain the proper ratios of EC and PH and to avoid diseases.
Greenhouses designated to cultivate crops using soil-less substrate must be equipped with high-quality climate, irrigation and fertigation control systems.
Comparison Chart
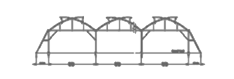
Top Gothic
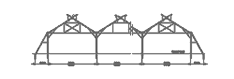
Top Max
Top Sawtooth
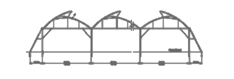
Top Tropical
Top Tunnels
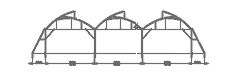
Top Koren
Top Nethouses
Shade net
Climate
Climate
Cold
Climate
Double
Double